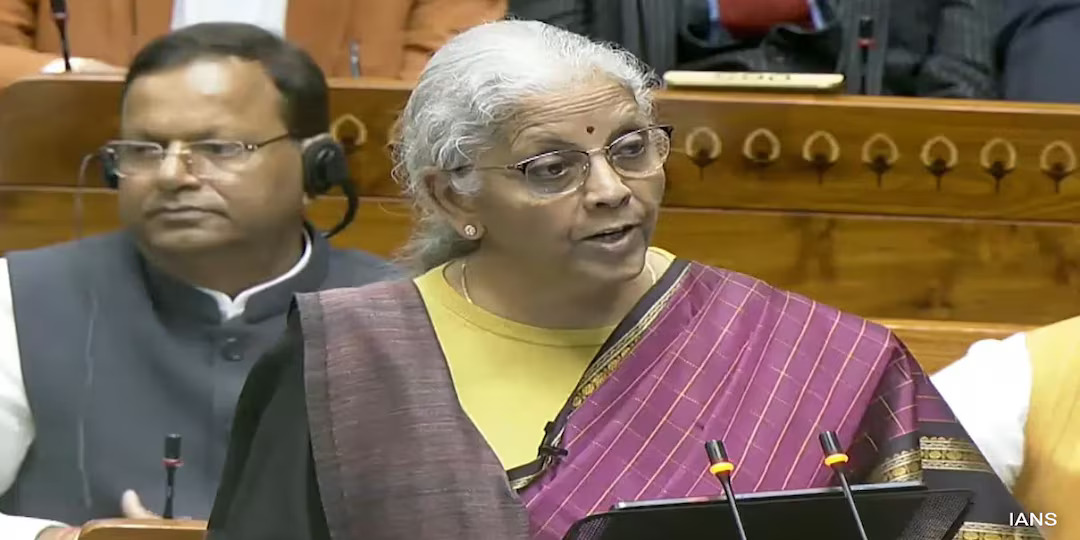
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Sunday, February 1, 2026, presented her ninth consecutive Union Budget in Parliament, making history as the first Union Budget to be presented on a Sunday. The Budget for the financial year 2026 27 focused on growth, technology, manufacturing and fiscal discipline, while keeping personal income tax slabs unchanged.
One of the major announcements was that the new Income Tax Act will come into effect from April 1, 2026. The government said the new law aims to simplify tax rules and make compliance easier for taxpayers. Sitharaman said the fiscal deficit for 2026 27 is estimated at 4.3 percent of GDP, slightly lower than the revised estimate of 4.4 percent for the current year. The total size of the Budget was placed at rupees 53.5 lakh crore.
The Finance Minister said the Budget is guided by three core duties, accelerating economic growth, fulfilling people’s aspirations and ensuring inclusive development across regions and communities under the vision of Sabka Vikas.
A key proposal was a tax holiday until 2047 for foreign companies offering global cloud services through data centres located in India. The move is aimed at strengthening India’s position as a global digital infrastructure hub. Technology featured prominently in the speech, with artificial intelligence mentioned eleven times, the highest ever in a Budget address.
Capital expenditure was increased to rupees 12.2 lakh crore, continuing the government’s push for infrastructure development. Sitharaman announced plans for seven high-speed rail corridors, new freight corridors, twenty national waterways and large-scale investments in smaller cities. The government also proposed dedicated corridors for rare earth minerals and a new industrial corridor along the east coast.
In the manufacturing sector, the government announced plans to revive two hundred old industrial clusters and introduced a rupees 10,000 crore growth fund for small and medium enterprises. The India Semiconductor Mission 2.0 was expanded with an allocation of rupees 40,000 crore. A separate rupees 10,000 crore scheme was announced to boost container manufacturing in India.
Healthcare and social welfare received attention with customs duty exemptions announced for seventeen cancer drugs and medicines used to treat seven rare diseases. The Finance Minister also announced a rupees 10,000 crore Biopharma Shakti programme to strengthen pharmaceutical manufacturing. New initiatives such as NIMHANS 2.0 and upgrades to mental health institutions were proposed to improve trauma and mental healthcare services.
In agriculture, Sitharaman announced targeted schemes to improve farmer incomes. These included a coconut development programme and support for cashew, cocoa and sandalwood cultivation. The government also proposed launching Bharat Vistar, a multilingual artificial intelligence-based platform to help farmers access data-driven agricultural guidance.
On taxation, while income tax slabs were left unchanged, several reforms were announced. These included extended deadlines for filing and revising tax returns, reduced penalties, a one-time six-month window for declaring foreign assets and exemption of interest awarded by Motor Accident Claims Tribunals from income tax. The Securities Transaction Tax on futures and options was increased.
The defence budget was raised to rupees 7.85 lakh crore, with rupees 2.19 lakh crore allocated for modernisation. Tourism, sports, creative industries and medical value tourism also received focused support through new institutes, training programmes and tourism circuits across different states.
The ruling Bharatiya Janata Party described the Budget as a forward-looking roadmap for a developed India, while opposition parties criticised it for failing to provide direct relief to the middle class. Market reaction during the Budget session was mixed, with equity indices seeing a sharp decline.
Overall, the Union Budget 2026 27 reflects continuity in fiscal consolidation, a strong focus on technology and manufacturing and long-term reforms aimed at positioning India as a major global economic and services hub by the year 2047.